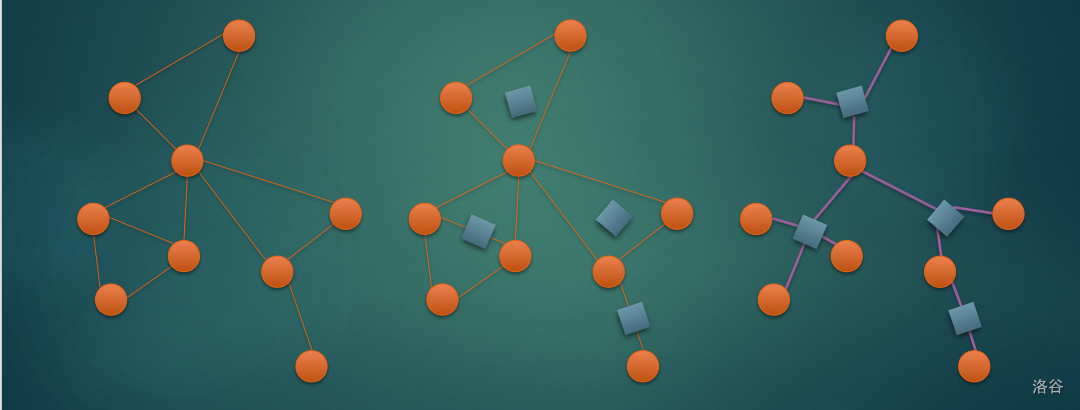
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
| #include"bits/stdc++.h"
#define re register
#define int long long
#define ls(p) tr[p].ls
#define rs(p) tr[p].rs
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5e5+10,inf=1e18;
int n,m,Q,cnt,tim,top,tot,rt,segcnt,id;
int a[maxn],head[maxn];
int dfn[maxn],low[maxn],stk[maxn];
vector<int> g[maxn<<1];
multiset<int> s[maxn];
struct edge{
int to,nxt;
}e[maxn<<1];
struct node{
int fa,dep,siz,hson,top,dfn,seq;
}t[maxn<<1];
struct tree{
int ls,rs,mn;
}tr[maxn<<2];
inline void add(int u,int v){
e[++cnt]={v,head[u]};
head[u]=cnt;
}
inline void tarjan(int u,int fa){
dfn[u]=low[u]=++tim;
stk[++top]=u;
for(re int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt){
int v=e[i].to;
if(!dfn[v]){
tarjan(v,u);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
if(low[v]>=dfn[u]){
g[++tot].push_back(u),g[u].push_back(tot);
int x;
do{
x=stk[top--];
g[tot].push_back(x),g[x].push_back(tot);
}while(x!=v);
}
}
else if(v!=fa) low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
}
inline void dfs1(int u,int fa){
t[u].fa=fa;t[u].siz=1;t[u].dep=t[fa].dep+1;
for(auto v:g[u]){
if(v==fa) continue;
dfs1(v,u);
t[u].siz+=t[v].siz;
if(!t[u].hson||t[v].siz>t[t[u].hson].siz) t[u].hson=v;
}
}
inline void dfs2(int u,int top){
t[u].dfn=++id;t[id].seq=u;t[u].top=top;
if(!t[u].hson) return;
dfs2(t[u].hson,top);
for(auto v:g[u]){
if(v==t[u].hson||v==t[u].fa) continue;
dfs2(v,v);
}
}
inline void up(int p){tr[p].mn=min(tr[ls(p)].mn,tr[rs(p)].mn);}
inline void build(int l,int r,int &p){
if(!p) p=++segcnt;
if(l==r){tr[p].mn=a[t[l].seq];return;}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(l,mid,ls(p)),build(mid+1,r,rs(p));
up(p);
}
inline void update(int l,int r,int pos,int val,int p){
if(l==r){tr[p].mn=val;return;}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(pos<=mid) update(l,mid,pos,val,ls(p));
else update(mid+1,r,pos,val,rs(p));
up(p);
}
inline int query(int l,int r,int L,int R,int p){
if(l>=L&&r<=R) return tr[p].mn;
int mid=(l+r)>>1,res=inf;
if(L<=mid) res=min(res,query(l,mid,L,R,ls(p)));
if(R>mid) res=min(res,query(mid+1,r,L,R,rs(p)));
return res;
}
inline int query(int u,int v){
int res=inf;
while(t[u].top!=t[v].top){
if(t[t[u].top].dep<t[t[v].top].dep) swap(u,v);
res=min(res,query(1,tot,t[t[u].top].dfn,t[u].dfn,1));
u=t[t[u].top].fa;
}
if(t[u].dep>t[v].dep) swap(u,v);
res=min(res,query(1,tot,t[u].dfn,t[v].dfn,1));
if(u>n) res=min(res,a[t[u].fa]);
return res;
}
signed main(){
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("1.in","r",stdin);
freopen("1.out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>Q;tot=n;
for(re int i=1;i<=n;++i) cin>>a[i];
for(re int i=1,u,v;i<=m;++i) cin>>u>>v,add(u,v),add(v,u);
tarjan(1,0),dfs1(1,0),dfs2(1,1);
for(re int i=2;i<=n;++i) s[t[i].fa-n].insert(a[i]);
for(re int i=n+1;i<=tot;++i) a[i]=s[i-n].empty()?inf:*s[i-n].begin();
build(1,tot,rt);
char op;int x,y;
while(Q--){
cin>>op>>x>>y;
if(op=='C'){
update(1,tot,t[x].dfn,y,1);
if(x==1){a[x]=y;continue;}
s[t[x].fa-n].erase(s[t[x].fa-n].lower_bound(a[x]));
s[t[x].fa-n].insert(y);
int mn=*s[t[x].fa-n].begin();
if(mn==a[t[x].fa]){a[x]=y;continue;}
update(1,tot,t[t[x].fa].dfn,mn,1);
a[t[x].fa]=mn,a[x]=y;
}
else cout<<query(x,y)<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
|